The Northrop B-2 Spirit, better known as the B2 bomber, is a marvel of modern aviation. Its sleek, bat-like design and stealth technology make it one of the most advanced warplanes ever built. On June 21, 2025, the B2 bomber took center stage in a U.S. military operation targeting Iran’s nuclear sites, showcasing its unmatched ability to strike deep, hardened targets. This article dives into the B2 bomber’s history, design, capabilities, and its critical role in the recent Iran bombing, exploring why it remains a cornerstone of U.S. airpower.
A Brief History of the B2 Bomber
The Northrop B-2 Spirit was born during the Cold War to counter Soviet air defenses. Designed in the 1970s as a stealth bomber, it first flew in 1989 and entered service in 1997. Built by Northrop Grumman, the B2 bomber was meant to deliver nuclear or conventional weapons deep into enemy territory without detection. Only 21 were made due to high costs, with 19 still active today. Its recent use in Iran proves it’s still a game-changer, capable of hitting targets no other plane can reach.
Origins in the Cold War
The B2 bomber began as a secret project to create a plane that could evade radar. The U.S. wanted a bomber to strike Soviet targets without being shot down. Northrop’s flying wing design, inspired by earlier models, used advanced materials to reduce its radar signature. By the late 1980s, the B2 bomber emerged as a stealth pioneer, though its $2 billion price tag per plane sparked debate. Its ability to fly undetected remains unmatched, as seen in Iran.
Evolution Over Decades
Since its debut, the B2 bomber has been upgraded with better radar, weapons, and navigation systems. It first saw combat in Kosovo in 1999, dropping precision bombs. Later missions in Iraq, Afghanistan, Libya, and Yemen honed its role in striking high-value targets. In 2025, the B2 bomber’s strike on Iran’s nuclear sites showed how upgrades keep it relevant, despite plans to replace it with the B-21 Raider by 2032.
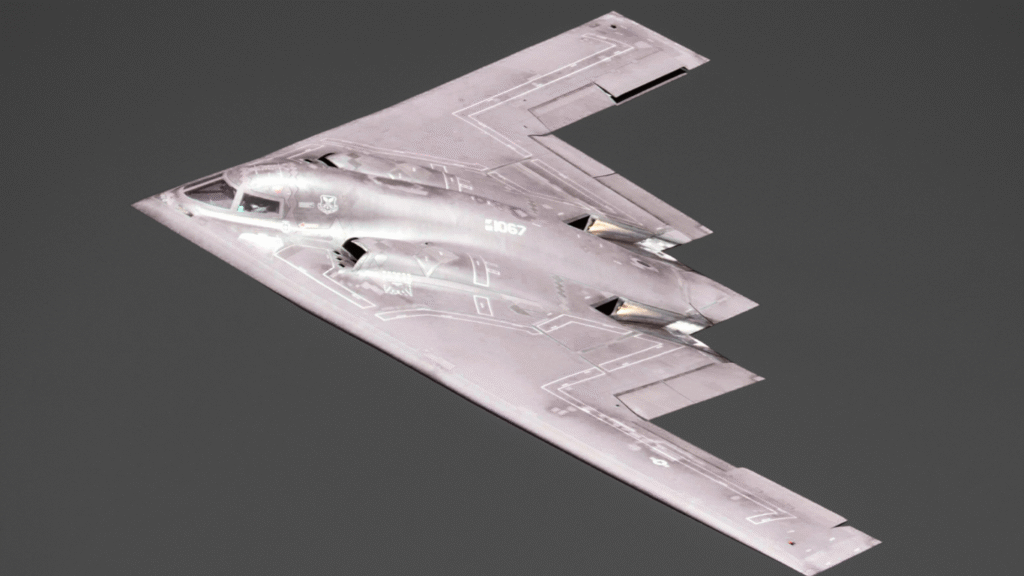
Design and Stealth Technology
The B2 bomber’s unique design sets it apart. Its flying wing shape, with no tail or fuselage, reduces radar detection. Special coatings and materials absorb radar waves, making it look like a small bird on enemy screens. The B2 bomber can carry heavy payloads over long distances, refueling mid-air for global reach. Its stealth was crucial in Iran, allowing it to penetrate defenses and hit buried nuclear facilities with precision.
Flying Wing Architecture
The B2 bomber’s bat-like shape isn’t just for looks. The flying wing design blends wings and body into one smooth surface, cutting radar reflections. Its engines are buried inside to hide heat signatures. This allowed the B2 bomber to slip through Iran’s weakened air defenses in June 2025, dropping massive bombs on Fordow. The design also improves fuel efficiency, letting it fly 6,000 miles without refueling, critical for long missions.
Stealth Features Explained
Stealth is the B2 bomber’s superpower. Radar-absorbing materials, curved surfaces, and low-heat emissions make it nearly invisible. Its radar cross-section is about 0.001 square meters, tiny compared to other planes. In Iran, this stealth let B2 bombers evade detection, striking nuclear sites before Iran could respond. The plane’s internal weapons bays keep bombs hidden, maintaining stealth during attacks, a key factor in its success against fortified targets.
Capabilities and Armament
The B2 bomber is a heavy hitter, carrying up to 40,000 pounds of weapons, from nuclear bombs to precision-guided munitions. It can strike 16 targets at once with GPS-guided bombs or deliver massive bunker-busters like the GBU-57 MOP. In Iran, the B2 bomber used these capabilities to destroy underground nuclear facilities, proving its ability to tackle the toughest targets. Its long range and two-person crew make it a versatile global strike platform.
Massive Ordnance Penetrator (MOP)
The GBU-57 MOP, a 30,000-pound bunker-buster, is the B2 bomber’s ultimate weapon. Designed to destroy deeply buried targets, it can penetrate 200 feet of concrete. In the Iran strikes, B2 bombers dropped six MOPs on Fordow, a nuclear site 300 feet underground, likely requiring multiple hits to collapse it. Only the B2 bomber can carry this bomb, making it essential for missions against hardened facilities like Iran’s nuclear plants.
Versatile Weapon Systems
Beyond the MOP, the B2 bomber carries a range of weapons, including JDAMs for precision strikes and nuclear bombs like the B83. Its internal bays hold up to 80 500-pound bombs or 16 larger ones, allowing flexible mission profiles. In Iran, the B2 bomber likely used JDAMs alongside MOPs to hit Natanz and Esfahan, showing its ability to tailor attacks to different targets, from surface buildings to underground bunkers.
Role in the Recent Iran Bombing
On June 21, 2025, B2 bombers struck three Iranian nuclear sites—Fordow, Natanz, and Esfahan—in a major U.S. operation. President Trump called it a “very successful attack,” targeting Iran’s nuclear program. The B2 bomber’s stealth and MOP bombs were critical, especially at Fordow, a fortified site. The mission, flown from Whiteman Air Force Base, Missouri, showed the B2 bomber’s global reach and precision, escalating U.S. involvement in the Israel-Iran conflict.
Mission Details and Execution
The B2 bombers flew 37 hours non-stop to Iran, refueling multiple times mid-air. Departing Whiteman AFB, they used stealth to bypass Iran’s degraded air defenses, weakened by prior Israeli strikes. Each bomber carried two MOPs, with six dropped on Fordow to ensure destruction. Additional JDAMs likely hit Natanz and Esfahan’s surface facilities. The B2 bomber’s precision ensured minimal collateral damage, though the strikes heightened regional tensions, with Trump threatening more if Iran retaliated.
Strategic Impact on Iran
The B2 bomber’s strikes aimed to cripple Iran’s nuclear ambitions. Fordow, buried under a mountain, was the primary target due to its uranium enrichment. The MOPs likely collapsed key tunnels, rendering it inoperable for years. Natanz and Esfahan, less fortified, suffered heavy damage to infrastructure. While Iran’s nuclear knowledge remains, the B2 bomber’s attack set back its program significantly, though experts warn it could rebuild without diplomacy, risking further conflict.
Challenges and Risks of B2 Operations
Operating the B2 bomber is no easy task. Its high cost, complex maintenance, and small fleet of 19 planes limit its use. Missions like Iran’s require extensive planning, with refueling tankers and fighter escorts to protect against threats. The B2 bomber’s stealth reduces risks, but Iran’s missiles could still target staging bases like Diego Garcia. The Iran strikes highlighted both the B2 bomber’s power and the logistical hurdles of deploying it in contested regions.
Logistical Demands
The B2 bomber’s Iran mission needed a massive support network. Eight refueling tankers supported the 37-hour flight, with each bomber requiring multiple mid-air refuelings. Staging from Whiteman AFB, rather than closer bases like Diego Garcia, added complexity but reduced vulnerability to Iranian missiles. The B2 bomber’s maintenance is also intensive, with each sortie requiring days of prep. These demands limit how often it can be used, even in critical missions like Iran.
Vulnerabilities in Contested Airspace
Despite its stealth, the B2 bomber isn’t invincible. Iran’s air defenses, though weakened, could still pose risks if not fully suppressed. Bases like Diego Garcia, 2,400 miles from Iran, are within missile range, as seen in earlier 2025 deployments. In the Iran strikes, Israeli attacks on Iran’s S-300 systems cleared the way for B2 bombers, but future missions could face denser defenses, requiring careful coordination with escorts and electronic warfare to ensure safety.
Global Reactions and Implications
The B2 bomber’s strikes on Iran sparked worldwide debate. Allies like Israel praised the U.S. action, while Iran vowed retaliation, raising fears of a broader war. Oil prices surged, and markets braced for instability. The B2 bomber’s role highlighted U.S. military dominance but also its willingness to escalate conflicts. Diplomats, including France, urged talks, but Iran’s internet blackout and hardline stance complicated efforts, leaving the region on edge.
Regional Tensions Escalate
Iran’s neighbors, including Saudi Arabia, backed the B2 bomber’s strikes, seeing Iran’s nuclear program as a threat. However, Iran’s proxies, like the Houthis, threatened U.S. ships, echoing their Red Sea attacks. The B2 bomber’s use signaled to Iran’s allies that the U.S. could strike anywhere, anytime. Yet, without a clear endgame, the strikes risk prolonging the Israel-Iran conflict, with the B2 bomber at the heart of future U.S. strategy.
Diplomatic Fallout
The B2 bomber’s attack closed doors to U.S.-Iran talks, with Tehran rejecting direct negotiations. European allies, pushing for diplomacy, criticized the timing, fearing it strengthened Iran’s hardliners. The B2 bomber’s success in damaging nuclear sites gave the U.S. leverage but also painted it as an aggressor in some eyes. Posts on X reflected public fear, with users calling the strikes a prelude to war, underscoring the B2 bomber’s role in shaping global perceptions.
The Future of the B2 Bomber
The B2 bomber remains vital, but its days are numbered. The B-21 Raider, a cheaper, stealthier successor, is set to replace it by 2032. Until then, the B2 bomber will handle high-stakes missions, like Iran’s, where stealth and heavy payloads are needed. Its recent success proves its worth, but rising costs and aging systems challenge its longevity. The B2 bomber’s legacy as a stealth pioneer will endure, even as new technology takes over.
Transition to the B-21 Raider
The B-21 Raider, now in testing, promises lower costs and advanced stealth. Unlike the B2 bomber, it’s designed for larger production, with 100 planned. The B2 bomber’s Iran mission showed why stealth bombers matter, but its $2 billion price and maintenance needs limit its future. The B-21 will build on the B2 bomber’s lessons, ensuring the U.S. retains global strike power as threats like Iran’s nuclear program persist.
Legacy of Stealth Innovation
The B2 bomber redefined air warfare with its stealth and precision. From Kosovo to Iran, it proved planes could strike deep without detection. Its radar-deflecting design inspired modern stealth tech, including the B-21. The B2 bomber’s role in Iran cemented its status as a symbol of U.S. might, but its high cost sparked debates about affordability. As it nears retirement, the B2 bomber’s impact on aviation and strategy will shape military thinking for decades.